Quck answer
Frogs are amphibians that have unique physical and biological characteristics that allow them to adapt to different environments. They have a smooth, moist skin that helps them breathe through their skin. Frogs also have strong legs that allow them to jump long distances and swim in water. They have a powerful tongue that they use to catch prey, and their eyes are positioned on the top of their head, giving them a wide field of vision. Additionally, frogs have a remarkable ability to regenerate lost limbs and even repair damaged organs. These features make frogs fascinating creatures to study and admire.
Wild Animals
From Mating to Metamorphosis: The Fascinating World of Frogs

Red-eyed tree frogs engage in sexual reproduction on a leaf in the rainforest. The male and female differ in size and color.
Photo by Mattias Klum/National Geographic/Getty Images
Frog reproduction is a topic that most people learn about in elementary school. However, not all frogs follow the same steps in their reproductive cycle. Despite this, some general rules apply to all frog species. For instance, all frogs reproduce sexually and hatch from eggs.
Most frogs fertilize their eggs outside the female’s body. During mating, the male and female assume a posture called amplexus, where the male climbs onto the female’s back and clasps his forelegs around her middle. This position ensures that the sperm reaches the eggs. Amplexus can last for hours or even days as the female releases one or several hundred eggs.
Some frog species exhibit sexual dimorphism, which means that males and females differ in body size and color. However, in some species, males and females look alike. To distinguish between the sexes, male frogs produce a release call when clasped by another male during mating season.
Frog eggs require moisture to develop. Most frogs abandon their eggs once fertilized. However, some species carry their eggs in their vocal sacs or abdomens, while others lay eggs in dry areas and keep them moist with water or urine. Depending on the species and the climate, eggs can hatch within a few days to a few weeks.
Most frogs begin life as tadpoles. While adult frogs are carnivorous, tadpoles can be vegetarians or omnivores. After hatching, tadpoles grow and develop. The transformation into a frog is called metamorphosis. During this transformation, the back legs begin to grow first, followed by the front legs. The tadpole’s internal organs also change, developing lungs and a digestive system that can accommodate an adult diet. The tail disappears as it is absorbed into the body. Once the froglet is ready to live on land, it has only a small tail left, which gradually disappears.
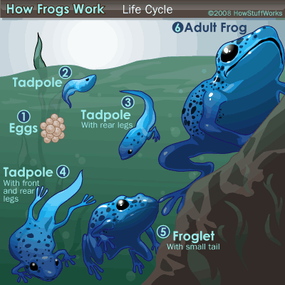
2008 HowStuffWorks
Most frog eggs and tadpoles are eaten by other animals, including fish and birds, which means that many don’t survive to adulthood. Even adult frogs have many enemies, including microscopic ones. In this article, we will explore some of the threats that frogs face and how the loss of these amphibians could impact human life. Despite their vulnerability, frogs are found on every continent except Antarctica and are often featured in stories and fairy tales. For example, in the Western world, the tale of the frog prince tells the story of a frog that transforms into a prince when kissed by a princess. This idea of transformation comes from the natural metamorphosis of tadpoles into frogs. Frogs are also associated with fertility in some cultures, possibly due to the noisy mating season and the large number of eggs females can lay. Despite their positive associations, the warty and sometimes grotesque appearance of frogs has led to them being portrayed as companions to witches in stories like “Macbeth.”
FAQ
1. What are some unique characteristics of frogs?
Frogs are amphibians that have several unique characteristics. They have moist skin that allows them to breathe through their skin, and they have webbed feet that help them swim. Frogs also have long, sticky tongues that they use to catch insects and other prey. They are cold-blooded and can change color to blend in with their surroundings.
2. How do frogs reproduce?
Frogs reproduce by laying eggs in water. The male frog will fertilize the eggs as they are being laid by the female. The eggs will then hatch into tadpoles, which will eventually grow legs and arms and become adult frogs.
3. What do frogs eat?
Frogs are carnivorous and eat insects, spiders, worms, and other small animals. They catch their prey by using their long tongues to quickly snatch them up.
4. How do frogs protect themselves from predators?
Frogs have several ways of protecting themselves from predators. They can change color to blend in with their surroundings, they can jump long distances to escape danger, and some species have toxic skin secretions that can make predators sick or even kill them.
5. What is the habitat of frogs?
Frogs live in a variety of habitats, including forests, swamps, and ponds. They need water to breed, so they are typically found near bodies of water. Some species of frogs can also live in drier environments, such as deserts.
6. How do frogs breathe?
Frogs breathe through their skin, which needs to be moist in order for them to absorb oxygen. They also have lungs, but they are not as efficient as the lungs of mammals. When a frog is on land, it will take in air through its nostrils and then pump air into its lungs by using its throat.
7. What are some common species of frogs?
Some common species of frogs include the American bullfrog, the green tree frog, the poison dart frog, and the northern leopard frog. There are over 7,000 species of frogs, so there is a lot of variety in their appearance and behavior.
8. How do frogs communicate?
Frogs communicate with each other through a variety of vocalizations, including croaks, grunts, and whistles. These sounds are used to attract mates, establish territory, and warn other frogs of danger.
9. How are frogs important to the ecosystem?
Frogs play an important role in the ecosystem as both predators and prey. They help control insect populations by eating large numbers of insects, and they are also an important food source for many other animals. Some species of frogs have even been used in medical research to help develop new drugs and treatments.





Leave a Reply