Quck answer
Termites are social insects that live in colonies and feed on cellulose-rich materials such as wood and plant debris. They have a highly organized social structure and divide labor among different castes, including workers, soldiers, and reproductive individuals. Termites are able to break down cellulose with the help of specialized bacteria in their gut, allowing them to digest and extract nutrients from otherwise indigestible materials. Their ability to break down wood and other cellulose-rich materials makes them important decomposers in many ecosystems, but also poses a threat to human structures if left unchecked. Understanding how termites work can help in developing effective methods for controlling and managing termite populations.
Wild Animals
Termites’ Physical Characteristics
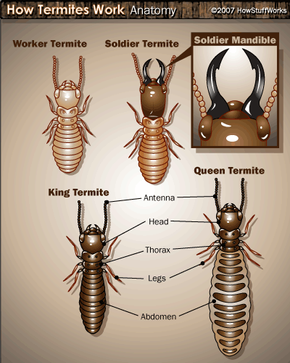
Termites are insects that can survive in almost any environment as long as the ground doesn’t freeze. They are closely related to cockroaches rather than ants, although they are often mistaken for the latter. All termite species are social and are divided into castes that have different physical features and jobs:
- Reproductives are responsible for laying eggs, and the king and queen are the primary reproductives in most colonies. Some species have secondary and tertiary reproductives to assist with egg-laying. Only the king and queen have eyes, and they are usually darker in color than the rest of the colony. The rest of the termites are blind and navigate using scent and moisture trails.
- Soldiers defend the nest from invaders, which are typically ants and termites from other colonies. They have large heads and strong, pincer-like mandibles, which are often darker than their bodies. Some species of soldiers can secrete toxic or sticky substances from their heads to kill or subdue intruders.
- Workers are milky or creamy in color and have smaller, saw-toothed mandibles that allow them to take small bites of wood and carry building materials. They are responsible for most of the work in the colony, including digging tunnels, gathering food, caring for young, and feeding the king, queen, and soldiers, who are unable to feed themselves. Workers and soldiers are sterile.
Termites feed on cellulose, which is a tough, resilient polymer found in plants. The compound is made up of glucose molecules, and humans cannot digest it. Similarly, termites cannot produce cellulase, the enzyme that breaks down cellulose. Instead, they rely on microorganisms that live in their hindgut, including bacteria and protozoans, to break down the cellulose into usable nutrients.

Termites are divided into two rough categories based on the types of organisms found in their hindgut. Higher termites have bacteria in their gut but no protozoans, while lower termites have both bacteria and protozoans. Additionally, termites can be categorized based on where they live. Subterranean termites build large nests underground, while many primitive termites form colonies in the wood they are consuming.
A termite colony is essentially a multigenerational family. The king and queen are usually monogamous, and workers and soldiers can be male or female in most species.
FAQ
1. What are termites?
Termites are social insects that belong to the order Blattodea. They are often called “white ants,” but they are not related to ants. Termites are known for their ability to consume wood and other cellulose materials, which can cause significant damage to buildings and other structures.
2. How do termites communicate?
Termites communicate through a variety of methods, including chemical signals, vibrations, and sounds. They use pheromones to signal the presence of food, danger, and other important information to other members of their colony. They also communicate through touch and antennation, which involves tapping antennae together.
3. What is a termite colony?
A termite colony is a highly organized social structure that can contain millions of individual termites. Each colony has a queen, workers, soldiers, and reproductive termites. The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers and soldiers carry out tasks such as foraging, building and maintaining the nest, and defending the colony from predators.
4. How do termites eat wood?
Termites have special bacteria in their gut that help break down cellulose, the main component of wood. They also have protozoa in their gut that further aid in digestion. Termites use their mandibles to break down wood into small pieces, which are then fed to the workers and other members of the colony.
5. How do termites build their nests?
Termites build their nests using a mixture of soil, saliva, and feces, which is known as “termite mud.” They use this material to construct intricate tunnels and chambers within the nest, which can be located both above and below ground. The nest provides protection from predators and helps regulate temperature and humidity levels.
6. How long do termite colonies last?
Termite colonies can last for many years, depending on the species and environmental conditions. Some colonies can survive for decades, while others may only last a few years. The queen is typically the longest-lived member of the colony, with some species living for up to 30 years.
7. What are the different types of termites?
There are over 2,700 species of termites, but they can be broadly categorized into three groups: subterranean termites, drywood termites, and dampwood termites. Subterranean termites are the most common and are found throughout the world. Drywood termites are found in warm, dry areas, while dampwood termites prefer wet environments.
8. How do you know if you have a termite infestation?
Signs of a termite infestation include the presence of mud tubes or tunnels near the foundation of your home, discarded wings near windows and doors, and visible damage to wood or other cellulose materials. It’s important to address a termite infestation as soon as possible to prevent significant damage to your home or other structures.
9. How can you prevent a termite infestation?
To prevent termites, it’s important to eliminate sources of moisture and wood contact around your home. This can include fixing leaky pipes, removing dead trees or stumps, and storing firewood away from your home. You can also use termite-resistant building materials and regularly inspect your home for signs of a termite infestation.
10. Can termites be beneficial?
While termites are often seen as destructive pests, they can also play a beneficial role in the ecosystem. Termites help break down dead plant matter and contribute to soil fertility. Some species of termites also provide a food source for other animals, such as birds and anteaters.
11. How are termites controlled?
Termites can be controlled through a variety of methods, including chemical treatments, baiting systems, and physical barriers. Chemical treatments involve applying insecticides to the soil around your home or directly to the affected wood. Baiting systems use slow-acting baits to target the entire colony, while physical barriers involve installing materials such as metal mesh or sand around the foundation of your home to prevent termites from entering.





Leave a Reply