
During the last nymph stage, cicadas create an exit tunnel to reach the surface and transform into adults by shedding their skin for the final time. Magicicada insects, which emerge in large numbers, have a higher chance of finding a mate. The dense emergence also serves as a predator-satiation defense. Researchers have identified 12 broods of 17-year cicadas and three broods of 13-year cicadas in deciduous forests, where trees shed their leaves in winter. Climate change may have far-reaching effects on cicadas, as longer growing seasons may change more 17-year cicadas into 13-year cicadas. Tracking cicada distributions over time requires detailed information.
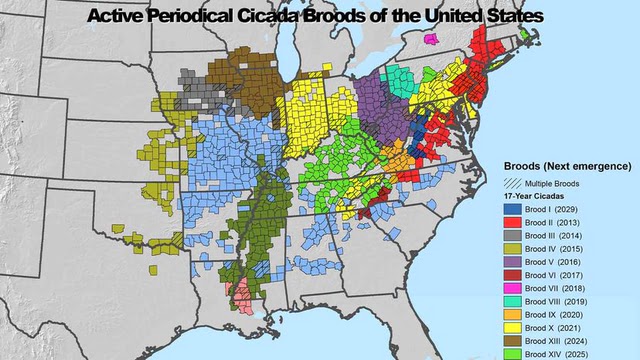
The U.S. Forestry Service has created a map that displays the locations and emergence dates of various cicada broods.
Join the Effort to Count Cicadas in Your Area
Volunteers are essential to this project due to the large population of periodical cicadas and their brief adult emergence period. To document the emergence of Brood X this spring, interested volunteers can download the Cicada Safari app and take photos, while following the research in real-time on www.cicadas.uconn.edu. Don’t miss out on this opportunity, as the next emergence of Broods XIII and XIX won’t occur until 2024.
This article was originally published on The Conversation and is shared under a Creative Commons license. The original article can be found here.
John Cooley, an assistant professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at the University of Connecticut, and Chris Simon, a professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at the same university, are the authors of this article and have received funding from the National Science Foundation and National Geographic.
FAQ
1. What are Brood X cicadas?
Brood X cicadas are a type of periodical cicada that emerge from the ground every 17 years. They are known for their loud and distinct buzzing sound and their large numbers, with billions of cicadas expected to emerge in the Eastern United States in 2021.
2. When will the Brood X cicadas emerge?
The Brood X cicadas are expected to emerge in May or June of 2021, depending on the weather conditions in each region. They typically emerge when the soil temperature reaches 64 degrees Fahrenheit.
3. Where will the Brood X cicadas be found?
The Brood X cicadas will be found in the Eastern United States, including parts of Delaware, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, North Carolina, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia, and Washington D.C.
4. Are the Brood X cicadas harmful?
The Brood X cicadas are not harmful to humans or pets. They do not bite or sting, and they are not poisonous. However, they can cause damage to young trees and shrubs, so it is important to protect them if you have recently planted new vegetation.
5. How long do the Brood X cicadas live?
The Brood X cicadas only live for a few weeks after they emerge from the ground. During this time, they mate and lay eggs before they die. The eggs then hatch and the young cicadas burrow into the ground to start the 17-year cycle all over again.
6. What should I do if I don’t want the cicadas around my home?
If you don’t want the cicadas around your home, there are a few things you can do. You can cover young plants with netting to protect them, avoid planting new vegetation until after the cicadas have gone, and keep your windows and doors closed to prevent them from entering your home.
7. Why do cicadas make so much noise?
Cicadas make noise as a way to communicate with other cicadas. The males make the loud buzzing sound to attract females for mating. The sound is created by a structure on the cicada’s body called a tymbal, which vibrates rapidly to produce the sound.
8. How do cicadas survive underground for 17 years?
Cicadas survive underground for 17 years by feeding on the sap of tree roots. They have long, piercing mouthparts that allow them to tap into the tree’s root system and extract the nutrients they need to survive. They stay underground to avoid predators and emerge en masse to increase their chances of survival during the brief period when they are above ground.
9. Can I eat cicadas?
Yes, cicadas are edible and are considered a delicacy in some cultures. However, it is important to properly prepare them before eating, as they can contain harmful bacteria if not cooked thoroughly.
10. Will the Brood X cicadas have any impact on the environment?
The Brood X cicadas play an important role in the ecosystem by providing food for birds and other animals. Their emergence also helps to aerate the soil and distribute nutrients throughout the ecosystem. However, they can cause damage to young trees and shrubs, so it is important to protect them if you have recently planted new vegetation.





Leave a Reply