Quck answer
Bioluminescence is the process by which living organisms produce light. It is a chemical reaction that occurs between a light-emitting molecule called luciferin and an enzyme called luciferase. When luciferin and luciferase come into contact with each other, they produce light. This process is used by many organisms, including fireflies, jellyfish, and certain types of bacteria, to attract mates, communicate with each other, and defend against predators. Bioluminescence is also used by scientists to study biological processes and to develop new technologies, such as biosensors and imaging tools for medical research.
Animal Facts
Light Production in Animals

The process of bioluminescence involves the fusion of two types of substances in a light-producing reaction, namely luciferin, a light-producing substance, and luciferase, an enzyme that speeds up the reaction. Some bioluminescent organisms use a photoprotein, which requires a charged ion to activate the light-emitting process. The reaction can be initiated by various triggers such as neurological, mechanical, chemical, or unknown factors.
Additionally, certain substances like oxygen or adenosine triphosphate (ATP) are also necessary for the reaction to occur. The luciferin-luciferase reaction can produce byproducts such as oxyluciferin and water.
The terms luciferin and luciferase are derived from the Latin word lucifer, meaning “light-bringer,” and are general terms rather than specific chemical names. Different species of bioluminescent organisms have varying luciferins and luciferases that act differently. For example, coelenterazine is a common luciferin in marine bioluminescence, while dinoflagellates that perform photosynthesis use a luciferin resembling chl. Some fish and shrimp produce their luciferin from their diet.
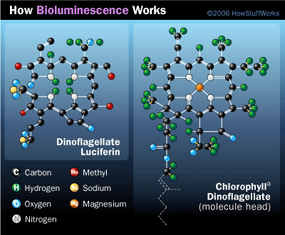
Dinoflagellate species that rely on photosynthesis for food have luciferin that is similar to chlorophyll.
Not all bioluminescent animals can produce their light. Further reading will explain the relationship between some organisms for their luminescence and how bioluminescence can benefit humans.
FAQ
1. What is bioluminescence?
Bioluminescence is a natural process in which living organisms emit light. This light is produced through a chemical reaction that takes place within the organism’s body. Bioluminescence can be found in a variety of organisms, including bacteria, fungi, fish, and insects.
2. How do organisms produce bioluminescence?
Organisms produce bioluminescence through a chemical reaction that involves an enzyme called luciferase and a molecule called luciferin. When luciferin is oxidized by luciferase, it produces energy in the form of light. The color of the light produced depends on the type of luciferin used.
3. What is the function of bioluminescence in organisms?
The function of bioluminescence varies depending on the organism. Some organisms use bioluminescence to attract mates or prey, while others use it to deter predators. Some organisms also use bioluminescence for communication or to navigate in the dark.
4. How is bioluminescence used in research?
Bioluminescence is used in research as a tool to study biological processes. Scientists can genetically modify organisms to produce bioluminescence, allowing them to observe and track the organisms in real-time. Bioluminescence imaging is also used in medical research to study diseases and drug efficacy.
5. Are there any risks associated with bioluminescence?
There are no known risks associated with bioluminescence. However, some organisms that produce bioluminescence, such as certain species of jellyfish, can be toxic to humans if ingested.
6. Can bioluminescence be artificially produced?
Yes, bioluminescence can be artificially produced. Scientists can create synthetic luciferin and luciferase molecules and use them to produce bioluminescence in a laboratory setting. Bioluminescent materials are also used in various applications, such as lighting and imaging.
7. What is the difference between fluorescence and bioluminescence?
Fluorescence and bioluminescence are both processes in which organisms emit light. However, fluorescence requires an external light source to excite the organism and produce light, while bioluminescence is a self-generated process that does not require an external source.
8. What is the future of bioluminescence research?
The future of bioluminescence research is promising. Bioluminescence has potential applications in fields such as medicine, environmental monitoring, and biotechnology. Scientists are also exploring the use of bioluminescence in developing new technologies, such as biosensors and bioluminescent displays.





Leave a Reply